Theme: Accentuating Current and Emerging Food Safety Issues
Food Safety Meet 2018
ME Conferences welcomes all the interested delegates and participants across the globe to attend International Conference on Food Safety and Health during August 30-31, 2018 in Dubai, UAE. The conference highlights the theme “Accentuating Current & Emerging Food Safety issues”. The conference coordinates comprise effective keynote lectures, plenary presentations, poster sessions, young researcher sessions from the distinguished scientists, researchers and talented students across the globe creating a platform for information exchange and knowledge transfer.
The lectures were designed on current and emerging areas of food safety research which include Food safety analysis, Food Quality management, Food Hazards, Food preservation, Food Toxicology, Risk assessment, Food administration, Food-borne diseases & Probiotics etc. We heartily welcome Entrepreneurs & business delegates from Food & Nutrition industries across the globe to share their latest technologies and processes ensuring food safety. The conference aims to discuss current challenges, which are main components in ensuring good health and the elimination of detrimental, fatal and cognitive ailments of mankind.
ME Conferences organizes 1000+ International Events inclusive of 300+ Conferences, 500+ Workshops and 200+ symposiums on numerous topics of Science and Technology across the world with support from one thousand additional scientific societies and Publishes 500+ Open access journals that contains over 50000 eminent personalities, supposed Scientists as editorial board members. ME Conferences has conducted skilled leading edge international conference globally within the fields of Nutrition, Food Safety and Technology.
Track 1: Food Safety and Packaging Technologies
Food safety is concerned with the handling, preparation, and storage of food in ways in which it can avoid food borne illness. The aim of the food safety is knowing the food safety risks long-faced in food service establishments, distinguishing risks in food service and finding ways in which to reduce them. Packaging continues to be one among the foremost necessary and innovative areas in food process. Altered by a leading expert within the field, and with its distinguished international team of contributors, Novel food packaging techniques provides an authoritative and comprehensive review of the key trends.
Track 2: Food Safety Laws and Regulations
From earliest times food has been significantly vulnerable to exploitation, and there's an extended history of food legislation with the aim of preventing consumers being either cheated or poisoned. Measures for the protection of the consumer against the adulteration of food and drink were among the earliest examples of social legislation. Despite the unquestioned improvement in food purity and in marketing practices caused by this legislation consumers are more and more uneasy about the security and quality of the modern food supply. Important elements of Food Safety include general principles of food law,food hygiene and Genetically Modified Organisms labeling. Proposes to update and extend legislative controls to ensure the safety of animal feed were also included in food safety regulatiuons.
Track 3: Food Frauds
The deliberate, substitution, addition, tampering or misrepresentation of food ingredients leads to food frauds. Food fraud is a hugely global issue. The most common type of includes false labelling, false certification, substitute ingredients, banned ingredients, food adultration, illegal products unfit for human consumption. Food Fraud isn't limited to these and there are a huge number of products that can be affected. The fact that this is such an international problem presents a real challenge for regulators. When food is crossing so many boundaries, it makes it very difficult for regulators to track. We need to bring together intelligence from around the world and get businesses to share information with each other. The analytical strategies usually used these days typically only examine one element of the food and so will only find one kind of fraud.
Track 4: Food Authenticity
The authenticity is an element of food and can be defined by the compliance of food to the referential genuine. The thought of authentic, outlined by something original, true, doubtless etc. applied to food, certifies that these products are from a certain origin in concordance with food standards and force rules and with the inscriptions of the presentation label. The authenticity, as a vicinity of quality elements, should be sure and certified and every and each commodity should have a name followed by a collection of legal features to avoid any variety of confusions on the market.
Track 5: Sustainability
Global demand for food is projected to extend by 70 per cent over future 40 years. Beside the necessity to extend food production is that the challenge of doing it in an exceedingly manner that doesn't impact on gas emissions, water quality, diverseness or fish stocks. The focus of this priority area is on sustainable, competitive and economical agri- & marine food production and process that includes: land-use optimisation, biology and non-food crops; wild fish gather and aquaculture; and also the manufacture of safe, value-added and innovative foods. Reduction of waste in food supply chains is a crucial sustainability issue. A lot of economical utilization and management of the resources and values created in food supply chains will contribute to rising competitiveness, and environmental and social responsibility. Simulation tools are usually used for supporting deciding on supply chain re style when logistical uncertainties are in place, building on their inherent modelling flexibility. Mostly, the underlying assumption is that product quality isn't influenced by or doesn't influence chain design. Clearly, this is often not true for food supply chains, as quality modification is intrinsic to the industry. We have a tendency to propose a brand new integrated approach towards logistics, sustainability and food quality analysis, and implement the approach by introducing a brand new simulation atmosphere.
Track 6: Food Traceability
Traceability systems are a crucial approach of minimizing risk and managing any issues quickly and efficiently. They track the trail of a product or ingredient from the initial supplier through all process and distribution stages, right to the end consumer. It allows to demonstrate and guarantee the quality of products and services, to promote the innovation of products and processes and to ensure the cognitive bases for decision-making. The current food labelling system cannot guarantee that the food is authentic, better quality and safe. For this reasons, traceability is applied as a tool to help among the reassurance of food safety and quality furtheras to accomplish consumer confidence.
Track 7: Food Hazards and HACCP
Track 8: Food Borne Diseases and Prevention
Track 9: Food Allergies and Intolerance
Track 10: Risk Analysis and Management
Track 11: Food Safety Surveillance System
Track 12: Food Safety Operations in Food Processing, Handling and Distribution
Track 13: Food Preservation and Quality Standard
Track 14: Food Safety in Retail Foods
Track 15: Food Contamination and Chemical Toxicology
Track 16:Microbiological and Chemical Aspects of Food Safety
Track 17: Foodomics Approaches in Food Safety
Track 18: Applied Nutrition
Track 19: Pediatric Nutrition
Track 20: Pest Management in Food Industry
Related Conferences:
- 20th International Conference on Nutrition, Food Science and Technology, April 16-17, 2018 Dubai,UAE
- 22nd World Nutrition and Pediatrics Healthcare Conference, July 16-18, 2018 Dubai, UAE
- World Congress on Food and Nutrition December 10-12, 2018 Dubai, UAE
- 3rd International Conferences on Food Chemistry & Nutrition May16-18,2018 Montreal, Canada
- 21st International Conference on Food & Nutrition July 25-26, 2018 Vancouver, Canada
- 4th International Conference on Food Chemistry and Technology November 5-7, 2018 Berlin, Germany
- 20th International Conference on Food Microbiology and Food Safety , March 22 - 23, 2018 Prague, Czechia
- 2nd Global Summit on Nutritional Science & Food Chemistry, May 24-25,2018,Valencia, Spain
- 10th Euro-Global Summit Aquaculture & Fisheries May 28-29, 2018London, UK
- 26th International ICFMH Conference - Food Micro 2018 September 3rd - 6th 2018
- 9th Global Summit on Food & Beverages: Green Food, Meat, Poultry, Sea & Dairy Food September 12- 13, 2018 Richmond, Virginia, USA
- Euro-Global Conference on Food Science, Agronomy and Technology, September 20-22, 2018, Rome, Italy
- 20th World Congress on Nutrition & Food Science, May 14-16, 2018 Tokyo, Japan
- 21st Euro-Global Summit on Food and Beverages March 8-10, 2018 Berlin, Germany
Summary:
Food safety is a subject describing handling, preparation, and storage of food in ways which forestall food-borne un healthiness. The incidence of two or more cases of an identical sicknesses resulting from the ingestion of a typical food is known as a Food-borne disease outbreak. This includes variety of routines that ought to be followed to avoid potential health hazards. During this approach food safety usually overlaps with food defence to forestall damage to consumers. The tracks within this line of thought are safety between industry and the market and then between the market and the client.
Importance & Scope:
International Conference on Food Safety and Health will be organized on August 30-31 in Dubai, UAE. The conference highlights the theme “Accentuating Current & Emerging Food Safety issues”. Food Safety and Health 2018 will discuss the latest research outcomes and technological advancements in the field of food safety, food processing, Food Hazards and HACCP, Risk analysis and management. The event is designed in a way to provide an exclusive platform for new researchers, scholars and educators to present and discuss the most recent innovations, trends, and concerns, practical challenges encountered and the solutions adopted in the field of food safety.
Food Safety Meet 2018 will comprise leading keynote speakers, session speakers, poster presenters who will be presenting their advanced research on the topics Food Processing. A variety of companies will display products and services that provide solutions for Food safety.
Why Dubai?
Dubai is a city in the United Arab Emirates, located within the emirate. The emirate of Dubai is located on the southeast coast of the Persian Gulf and is one of the seven emirates that make up the country. It has the most population in the UAE (2,106,177) and the second-largest land territory by area (4,114 km2) after Abu Dhabi. Is one of the few cities in the world that has withstood such a rapid conversion- from a courteous beginning as a pearl-diving centre - to one of the fastest growing cities on earth. Dubai these days is a business enterprise, trade and supply hub and has attained itself the name of being the ‘gateway between the east and therefore the west'. It is conjointly thought of dynamic nucleus of the Arabian Gulf region.
Dubai is without a doubt a destination of the 21st century. Read any article about the fastest growing city in the region and it’s almost guaranteed you’ll see the words ‘ambitious’, ‘record-breaking’ and ‘staggering’. This meteoric growth has not gone unnoticed, and each year thousands of expats arrive to claim a slice of the action.
Arab region when it comes to food safety and Dubai has always been at the forefront of all food safety-related initiatives — whether it is highly effective awareness campaigns, continuous and multiple rounds of inspections to ensure food safety or international conferences and exhibitions with the involvement of global experts in food safety.
Market Research:
The global marketplace for food safety testing could be a extremely fragmented one because of presence of many tiny and medium sized companies that are competitor with massive players. In 2016, the top 5 players in the international food safety market accounted for mere 200th of the general share within the market and it's extremely unlikely for any company to return below consolidation. That being mentioned, the players in operative within the world market are expected to profit from the new opportunities by providing premium services within the potential market landscape of upcoming companies. Some of the key players within the international food safety testing market include names like Eurofins Scientific SE, SGS SA, Thermo Fisher Scientific inc., Bio-Rad Laboratories, and Intertek group Plc. among others.
Target audience:
Food Safety and Health aims to bring together leading Academic scientists, NGO professionals, Food Agronomists, Food Policy makers and regulators, Researchers and Research scholars, students, dietician’s to exchange and share their experiences and research results; about all aspects of Food Safety, Food processing, Nutrition, Public Health and Economic regulations. It also provides the premier interdisciplinary and multidisciplinary forum for researchers, practitioners and educators to present and discuss the most recent innovations, trends, and concerns, practical challenges encountered and the solutions adopted in the field of Food Safety, Nutrition, Public Health and Global Economics.
Food Safety and Health 2018 will comprise leading keynote speakers, session speakers, poster presenters who will be presenting their research different topics related to Food safety and health aspects.
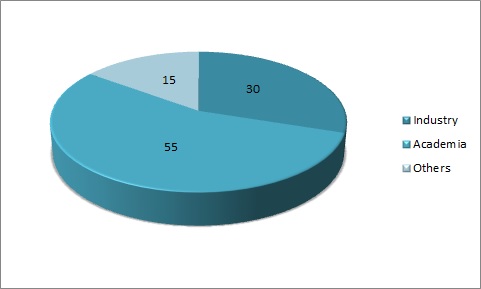
Target audience:
Industry 30%
Academia 55%
Others 15%
Figure 1: Target Audience
Food Safety Associated Universities in World:
- University of Valencia, Spain
- University of Helsinki, Finland
- University of Vienna, Austria
- Stockholm University, Sweden
- Queens University, Ireland
- University of Gothenburg, Sweden
- University of Bergen, Norway
- York University, UK
- University of Glasgow, Scotland
- University of Bern, Switzerland
- Uppsala University, Sweden
- University of Dundee, Scotland
- University of Hull, UK
- University of Cambridge, UK
- University of Southampton, UK
- University of Sunderland, UK
- University of Oxford, UK
- Aarhus University, Denmark
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology, USA
Food Safety Associated Universities in Middle East :
- Damascus University, Syria
- TEL AVIV UNIVERSITY, Israel
- LEBANESE INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY, Lebanon
- Yildiz Technical University, Istanbul
- Cyprus University of Technology
- Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Iran
- Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Iran
Food Safety Associated Universities in UAE:
- Canadian University of Dubai, Dubai
- United Arab Emirates University, UAE
- BITS Pilani, Dubai
- Amity University, Dubai
- International centre for Training and Development
- Manipal University Dubai
Figure 2: list of Universities
Companies Associated with food Industries:
- National Food products company
- United foods PSC
- SOLICO Food industries
- Global food industries
- Federal foods LLC
- Sunlmpex Biz
- Emirates Industrial & Trading Co Ltd
- Dabur International Ltd
- UB Gulf FZE
- Windsor Foodstuff Factory Ltd
- National Food Industries LLC (NFI)
- Yakult Honsha Co., LTD
Food Safety Consultants in Dubai
- MRS International Food Consultants
- GHP Group of Companies
- GHP Food Testing & Calibration Lab
- Bright Well quality Consultants
- Apex Food Consultants
- Al Safa Consultancy and Hospitality Services
- Sanbook Quality Consultancy
- Food Control Department of Dubai Municipality
Food Safety Software
- Safefood 360°
- Food Safety Management Software –EtQ
- SafetyChain Software
- TrackWise
- N2N Global
- eFood
- FoodLogiQ
- CSB-System
- Nutraid
- N2N Global
Top Independent Commercial Food Safety Labs
- NSF International
- AGES - Austrian Agency for Health and Food Safety
- Galbraith Laboratories Inc.
- LabiotestSrl
- LRQA Limited
Companies Associated with Food Safety
- Hygiene Expert
- 3M
- Food Standards Agency
- Qiagen
- European Safety Bureau
- MAS Environmental
- SAI Global
- Dacom
- LGC Standards
- A-Zone Technologies Ltd
- Waters Corporation
- Microbac Ltd
- Modern Water - Monitoring Division
- RVSL Certifications Ltd.
- Bibby Scientific
- Environmental Scientifics Group
- Aura Sustainability
- Radiant Industrial Solutions, Inc.
Related Societies & Associations
Globally:
- Good Food Society, UK
- The Food society, USA
- French Broad Preservation Association, France
- Slow Food, Italy
- ISEKI-Food Association, Europe
- IUFoST International Union of Food Science and Technology, Europe
- National Association of Specialty Food, USA
Asia/pacific:
•Japan Society of Nutrition and Food Science, Japan
•The Australian Institute of Food Science Technology, Australia
•Asian Food Safety and Security Association, Bangladesh
•Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI),India
•State Food and Drug Administration of China, China
Middle East:
•Abu Dhabi Food Control Authority, UAE
•Egyptian Food Safety Information Centre (EFSIC), Egypt
•The Arab Centre for Nutrition, BAHRAIN
•HEALTH & SAFETY SOCIETY
•Qatar Foundation (QF) Food and Nutrition Services, Qatar
•Saudi Food and Drug Authority, Saudi Arabia
•Middle East Gases Association
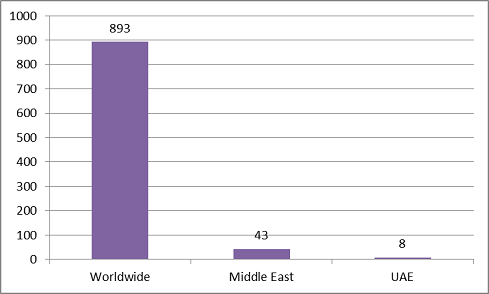
Figure 3: Associations & Societies
Projections: Growth by next 5-10 years:
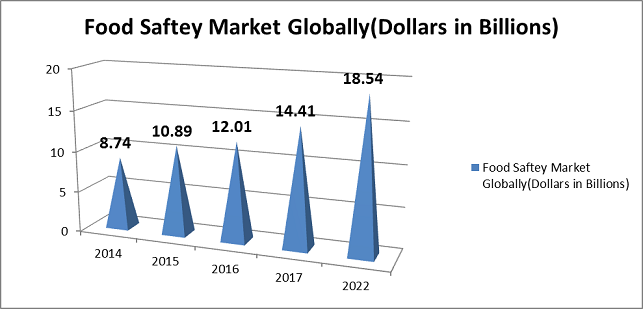
The food safety market was valued at USD 12.01 Billion in 2016. It's projected to grow at a powerful CAGR of 7.60% from 2017, to achieve 18.54 Billion by 2022. The global food safety testing market is expanding with considerable growth potential over the next five years. The global food safety testing market is increasing with appreciable growth potential over the succeeding 5 years. The expansion of this market is attributed to international rise in foodborne outbreaks, advancements in testing technologies, globalisation of food supply, and rigorous international food safety laws. The key players within the international food safety market are expected to concentrate upon additional attention from the customers by keeping a detailed eye on the quickly altering patterns of testing, enhancing their product at a similar time therefore as to provide precise tests. Establishing a robust brand is also projected to help these market players to sustain their consumer base.
Figure 4: Food Safety market
Related Societies:
Europe: Society of Food Hygiene and Technology (SOFHT), Norwegian Food Safety Authority, European Food Safety Authority, UK Food Associations, Safe Foods, Microbiological Safety of Food Funders Group, Federal Ministry of Food Agriculture and Consumer Protection, Food Standards Agency, Food and Rural Affairs
USA: International Association for Food Protection, Food and Agricultural Organization, Association of Food Industry, American Society for Nutrition, National Food Product Associations, Food Packaging Association, Food Processing Supplier Association, Flexible Food Packaging Association, National Food Processor Association, New Jersey Processing Association, Specialty Food Association,
Asia: Chinese American Food Society, Asia Pacific American Food Society, Nutrition Society of Malaysia, Food Society, Asia Pacific American Food Society, The Thai Packaging Association, Taiwan Frozen Food Processor Association, Food Safety South East Asia World Health Organization, Food Technology Asia, Singapore Food Manufacturing Association, Michigan Food Processors Association, Midwest Food Processors Association (MWFPA), Chinese American Food Society, Agricultural and Food Marketing Association, Probiotic Association of India, European Association of Agricultural Economists, United Arab Emirates Association for Food Protection
Conference Highlights
- Food Safety and Packaging Technologies
- Food Safety Laws and Regulations
- Food Frauds
- Food Authenticity
- Food Sustainability
- Food Traceability
- Food Hazards and HACCP
- Food Borne Diseases and Prevention
- Food Allergies and Intolerance
- Risk Analysis and Management
- Food Safety Surveillance System
- Food Safety Operations in Food Processing, Handling and Distribution
- Food Preservation and Quality Standard
- Food Safety in Retail Foods
- Food Contamination and Chemical Toxicology
- Microbiological and Chemical Aspects of Food Safety
- Foodomics Approaches in Food Safety
- New solutions for Identifying Emerging Risks
- Applied Nutrition
- Pest Management in Food Industry
- Dairy Technology
- Pediatric Nutrition
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | August 30-31, 2018 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Food: Microbiology, Safety & Hygiene
- Journal of Nutrition & Food Sciences Open Access
- Journal of Food Processing & Technology
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by